Home » All posts
27 May 2016
How to deactivate TDPO obsolete backups without TDPOSYNC utility ?
Tivoli Data Protection for Oracle (TDPO) backups will have unique version of backup stored in TSM server storage and that will be an active version. Any future backups will not be dependent on the old backups and all the backup objects will be in active version because each backup piece is stored under different filespace name and also the default retention setting for TDPO backups is 1,0,0,0. To know more about troubleshooting TDPO backups check the TDP tutorials in this website.
In order to expire the old TDPO/RMAN backups, DBA team need to regularly run the TDPOSYNC utility to mark the previous backups as expired as per the their RMAN retention settings and allow TSM server to delete the obsolete backups from TSM server storage.
However, in some environments people doesn't run the TDPOSYNC utility in regular intervals and since active backup data is not managed by TSM inventory expiration policies, the data is not deleted automatically, and uses server storage space indefinitely. As a TSM admin, we get worried about the storagepool free space when this kind of situation occurs.
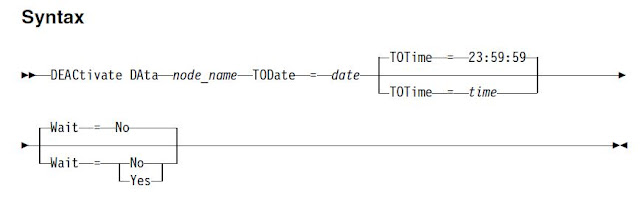
To address this kind of situation and to free the storage space that is used by obsolete active data which is not needed, you can deactivate the data. This feature is enabled from TSM V7.1.3 and we can deactivate the obsolete active TDPO backups by providing the DATE before which all backups to be deactivated.
When you run the deactivation process, all active backup data that was stored before the specified date becomes inactive. The data is then deleted as per the retention settings and it cannot be restored. In this way, you can free storage space on the Tivoli Storage Manager server without the need of TDPOSYNC utility or help from DBA team.
Example: deactivate data PRD_TDPO todate=01/01/2016
The DEACTIVATE DATA command affects only the files that were copied to the server before the specified date and time. Files that were copied after the specified date are still accessible, and the client can still access the server. This command applies only to application clients that protect Oracle databases.
Automatic and controlled decommissioning of TSM client node
The conventional approach which we are following from many days to delete a node and its backups from TSM server storage is by following the DECOMMISSIONING NODE process. In this process, once we get an approval to delete a node and its backup data we dissociate that node from all the backup schedules, then we lock the node and delete all the filespaces associated to that node and then eventually we end-up removing node from the TSM inventory. This process needs TSM administrator's monitoring and intervention.
When you start the decommission process, the server locks the client node to prevent it from accessing the server. Files that belong to the client node are gradually deleted, and then the client node is deleted. You can decommission BAclient node and as aswell as TDP & NAS nodes with this command. Remember that for decommisioning a VM node we have a separate command (DECOMMISSION VM).
Also we cannot run this command on client node that is configured for replication.We need to remove the client node from replication by using the REMOVE REPLNODE command before decommissioning this kind of node..
- This process will delete all schedule associations for the client node. Schedules are no longer run on the client node. This action is equivalent to issuing the DELETE ASSOCIATION command for every schedule with which the client node is associated.
- Next, it prevents the client from accessing the server. This action is equivalent to issuing the LOCK NODE command.
- Next, the client node data is no longer backed up to the server. Data that was backed up before the client node was decommissioned is not immediately deleted from the server. However, all backup file versions, including the most recent backup will be now marked as inactive copies. The client files will be retained as per the retention settings.
- Once all client backup and archive file copies are removed from server storage, Tivoli Storage Manager deletes the file spaces that belong to the decommissioned node. This action is equivalent to issuing the DELETE FILESPACE command.
- After all file spaces for the decommissioned node are deleted, the node definition is then deleted from the server. This action is equivalent to issuing the REMOVE NODE command.
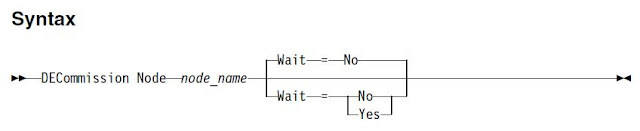
DECOMMISSION NODE
You should use this command to remove normal FILE-LEVEL node, TDP node or NAS node from TSM server. Any backup data that is stored for the client node expires according to policy settings unless you explicitly delete the data.
Example: decommission node ecom_prod
Please note that this action cannot be reversed and causes deletion of data. Although this command does not delete the client node definition until after its data expires, you cannot recommission the client node. After you issue this command, the client node cannot access the server and its data is not backed up. The client node is locked, and can be unlocked only to restore files.
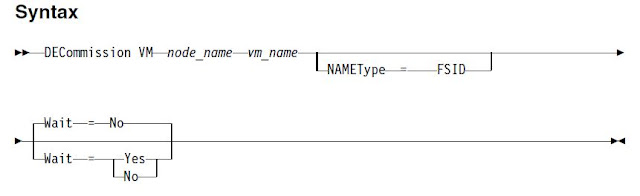
DECOMMISSION VM
You should use this command to initiate a controlled removal of the virtual machine file spaces from the server. This command will mark all data that was backed up for the virtual machine as inactive, so it can be deleted according to the data retention policies.
After all data that was backed up for the virtual machine expires, the file space that represents the virtual machine is deleted. The DECOMMISSION VM command affects only the virtual machine that you identify. The data center node, and the other virtual machines that are hosted by the data center node are not affected by this command.
Example: decommission vm salesvm