What is TSM Collocation ?
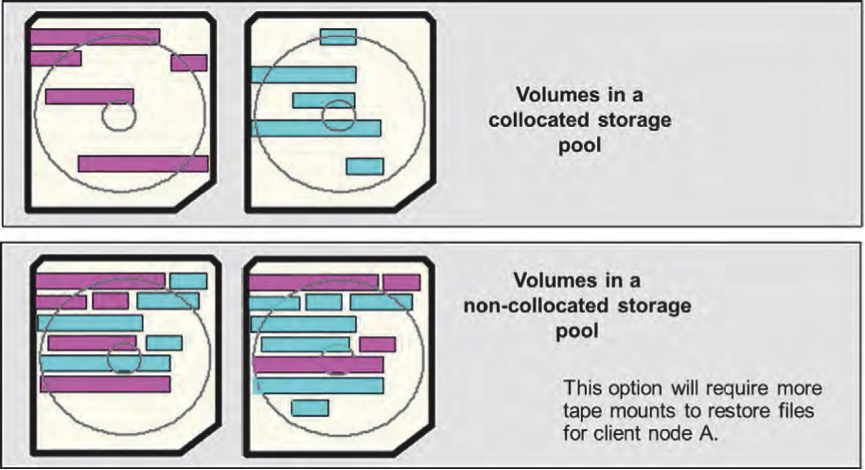
Collocation is the process by which the server minimizes the number of sequential access storage volumes to keep files of a single client node or file space of a client node. You can set collocation for each sequential access storage pool when you define or update the pool.
Image Source: IBM
By using collocation, you reduce the number of volume mount operations, and the amount of time searching database entries when users restore, retrieve, or recall multiple files. Thus, collocation improves access time for these operations. If collocation is enabled and reclamation occurs, the server tries to reclaim the files for each client node or client file space onto a minimal number of volumes. Collocation cannot collocate data that is already in a storage pool volume. The following options are available for collocation when you use the define stgpool or update stgpool commands
- No
- Node
- File space
- Group by node
- Group by file space
Collocation of active data
- Writing data to multiple pools by using simultaneous write.
- Copying data to an active-data pool by using the COPY ACTIVEDATA command. Only active versions of backup data are copied from a primary storage pool to an active-data pool. You use the following command
copy activedata primary_pool_name activedata_pool_name
How collocation process select volumes ?
Setting COLLOCATION=NODE causes Tivoli Storage Manager to try to put data for one node on as few volumes as possible.
Setting COLLOCATION=FILESPACE causes Tivoli Storage Manager to try to put data for file space for one client node on as few volumes as possible.
Volume selection criteria for COLLOCATION=NODE
- A volume that contains files from the same client node.
- An empty, predefined volume.
- An empty, scratch volume.
- Among volumes that contain data, the one with the most free space.
Volume selection criteria for COLLOCATION=FILESPACE
- A volume that contains files from the same file space of that client node.
- An empty, predefined volume.
- An empty, scratch volume.
- A volume that contains data from the same client node.
- Among volumes that contain data, the one with the most free space.
Collocation by groups of nodes
Collocation by group provides the following benefits. You must update the storage pool to use collocation by group.
- Reduce unused tape capacity, with more collocated data on individual tapes.
- Minimize mounts of target volumes.
- Minimize database scanning and reduce tape passes for sequential-to-sequential transfer.
- Minimize database scanning, which reduces tape passes for sequential-to-sequential transfers, such as reclamation.
Also Read: Tips to fix the TSM server startup problems
Use the define collocgroup command to define the group of nodes or filespaces for collocation
Use the define collocgroup command to define the group of nodes or filespaces for collocation
define collocgroup groupname
Use the define collocmember command to add a client node to a collocation group
define collocmember groupname node1,node2
After you define groups of nodes, the server can collocate data according to these groups.
Collocation by groups of file spaces
Similarly, use the define collocgroup command to define the group of nodes or filespaces for collocation
define collocgroup groupname
Use the define collocmember command to add a client node to a collocation group
define collocmember groupname filespace1,filespace2

0 Comment to "5.3 IBM Tivoli Storage Manager Collocation Overview"
Post a Comment